Ankron Water Services GmbH continues testing of indicative tools for commissioning tests of ballast water management systems. During the current survey another fluorometric devices for the 10-50 µm size fraction of organisms was tested.
Ankron Water Services is performing a survey with various indicative tools. This time Hach BW 680 was tested.
1. Background
The D-2 Standard gives the discharge limits for living organisms in ballast water (Table 1).
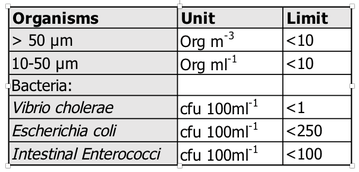
All ballast water management systems have to operate within this threshold. This is tested during the Type Approval test of the treatment system as well as during commissioning. The commissioning test is aiming to verify whether a type approved ballast water treatment system is performing properly after installation. Commissioning tests are mandatory from October 2021 on but MEPC encourages the flag administrations to implement the new requirement as soon as possible. For Singapore flagged vessels it is already required from 8th September 2019 on (MPA circ. 09/2019). As per BWM.2/Circ.42/Rev. 1 indicative tools can be used for commissioning testing to determine if the D-2 Standard can be met (see Table 2 for overview of 10-50 µm indicator).
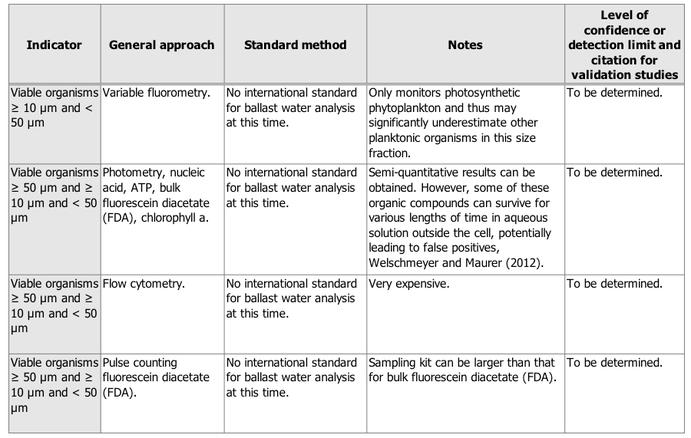
In order to be compliant with the D-2 discharge standard the number of viable organisms in the size range 10-50 µm has to be below 10 org/mL. The risk estimation of indicative tools gives an indication whether this threshold was met. Therefore, indicative methods are a great tool for a quick scan of the sample, but it should be noted that they won’t give an actual number of organisms in the sample. For that reason, they cannot be used for type approval testing but are suitable for commissioning tests were an indicative result is in accordance with the current requirements.
2. Experimental
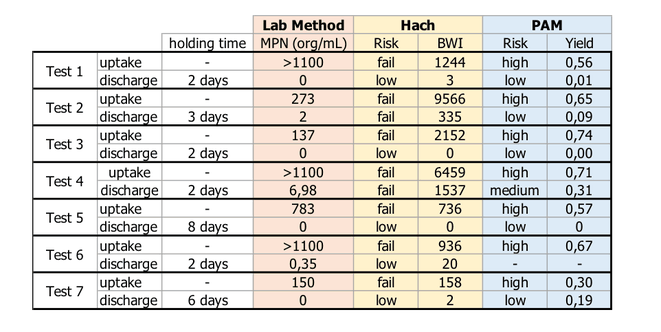
Untreated ballast water was collected upon uptake and treated ballast water during discharge. The samples were analyzed with one indicative method and compared to the lab method MPN (most probable number) and a Pulse-Amplitude-Modulation fluorometer measurement (PAM). The ballast water was treated with a low-pressure UV based treatment system. The performance of the Hach BW 680 can be seen in Table 3.
3. Ankron´s evaluation of the Hach BW 680
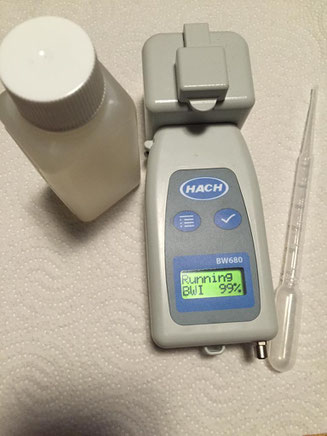
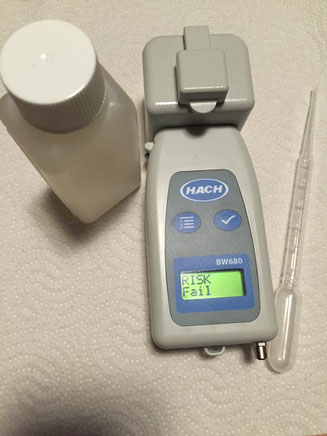
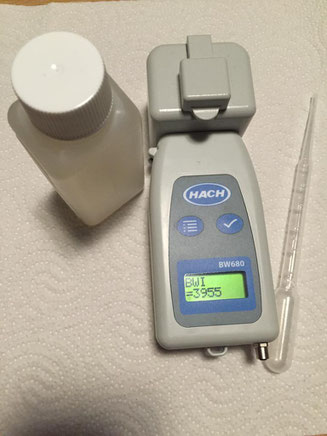
The results of the Hach BW 680 were in accordance with the lab method and the PAM measurement in 12 out of 14 trials. In two cases the discharge value failed according to BW 680 but met the D-2 values according to the lab method. The tested tool is very small, simple to use, robust, transportable and gives a result within a few minutes (Figure 1). It has no option for size separation. If the sample is taken after the plankton net and no additional filtration step is applied, all phytoplankton smaller 50 µm is measured. Due to the small size and straightforwardness the Hach BW 680 can come in handy when many samples have to be screened in different locations.
4. Outlook for indicative tools
A new regulation for verification of ballast water compliance monitoring devices is under development. It proposes a thorough validation procedure for indicative tools to be used for commissioning testing. Ankron Water Services GmbH and its partners are preparing for the announced validation tests to provide reliable results as independent testing organization.
written by Dr. Claudia Dreszer
